1. 方法概述
方法(method)是将具有独立功能的代码块组织成为一个整体,使其具有特殊功能的代码集
注意:
- 方法必须先创建才可以使用,该过程成为方法定义
- 方法创建后并不是直接可以运行的,需要手动使用后,才执行,该过程成为方法调用
2. 方法的定义和调用
2.1 无参数方法定义和调用(掌握)
定义格式:
1
2
3
| public static void 方法名 ( ) {
}
|
范例:
1
2
3
| public static void method ( ) {
}
|
调用格式:
注意:方法必须先定义,后调用,否则程序将报错
2.2 方法调用过程图解(理解)

- 总结:每个方法在被调用执行的时候,都会进入栈内存,并且拥有自己独立的内存空间,方法内部代码调用完毕之后,会从栈内存中弹栈消失。
2.3 无参数方法的练习(应用)
需求:设计一个方法用于打印两个数中的较大数
思路:
- ①定义一个方法,用于打印两个数字中的较大数,例如getMax()
- ②方法中定义两个变量,用于保存两个数字
- ③使用分支语句分两种情况对两个数字的大小关系进行处理
- ④在main()方法中调用定义好的方法
代码:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
| public class MethodTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
getMax();
}
public static void getMax() {
int a = 10;
int b = 20;
if(a > b) {
System.out.println(a);
} else {
System.out.println(b);
}
}
}
|
3. 带参数方法定义和调用
3.1 带参数方法定义和调用(掌握)
定义格式:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
|
public static void 方法名 (参数1) {
方法体;
}
public static void 方法名 (参数1, 参数2, 参数3...) {
方法体;
}
|
范例:
1
2
3
4
5
6
| public static void isEvenNumber(int number){
...
}
public static void getMax(int num1, int num2){
...
}
|
注意:
- 方法定义时,参数中的数据类型与变量名都不能缺少,缺少任意一个程序将报错
- 方法定义时,多个参数之间使用逗号( ,)分隔
调用格式:
方法调用时,参数的数量与类型必须与方法定义中的设置相匹配,否则程序将报错
3.2 形参和实参(理解)
形参:方法定义中的参数。等同于变量定义格式,例如:int number
实参:方法调用中的参数。等同于使用变量或常量,例如: 10 number
3.3 带参数方法练习(应用)
需求:设计一个方法用于打印两个数中的较大数,数据来自于方法参数 }
思路:
- ①定义一个方法,用于打印两个数字中的较大数,例如getMax()
- ②为方法定义两个参数,用于接收两个数字
- ③使用分支语句分两种情况对两个数字的大小关系进行处理
- ④在main()方法中调用定义好的方法(使用常量)
- ⑤在main()方法中调用定义好的方法(使用变量)
代码:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
| public class MethodTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
getMax(10,20);
int a = 10;
int b = 20;
getMax(a, b);
}
public static void getMax(int a, int b) {
if(a > b) {
System.out.println(a);
} else {
System.out.println(b);
}
}
}
|
4. 带返回值方法的定义和调用
4.1 带返回值方法定义和调用(掌握)
定义格式
1
2
3
| public static 数据类型 方法名 ( 参数 ) {
return 数据 ;
}
|
范例
1
2
3
4
5
6
| public static boolean isEvenNumber( int number ) {
return true ;
}
public static int getMax( int a, int b ) {
return 100 ;
}
|
注意:方法定义时return后面的返回值与方法定义上的数据类型要匹配,否则程序将报错
调用格式
1
2
| 方法名 ( 参数 ) ;
数据类型 变量名 = 方法名 ( 参数 ) ;
|
注意:方法的返回值通常会使用变量接收,否则该返回值将无意义
4.2 带返回值方法练习(应用)
需求:设计一个方法可以获取两个数的较大值,数据来自于参数
思路:
- ①定义一个方法,用于获取两个数字中的较大数
- ②使用分支语句分两种情况对两个数字的大小关系进行处理
- ③根据题设分别设置两种情况下对应的返回结果
- ④在main()方法中调用定义好的方法并使用变量保存
- ⑤在main()方法中调用定义好的方法并直接打印结果
代码:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
| public class MethodTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int result = getMax(10,20);
System.out.println(result);
System.out.println(getMax(10,20));
}
public static int getMax(int a, int b) {
if(a > b) {
return a;
} else {
return b;
}
}
}
|
5. 方法的注意事项
5.1 方法的注意事项(掌握)
方法不能嵌套定义
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
| public class MethodDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
}
public static void methodOne() {
public static void methodTwo() {
}
}
}
|
void表示无返回值,可以省略return,也可以单独的书写return,后面不加数据
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
| public class MethodDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
}
public static void methodTwo() {
return;
}
}
|
5.2 方法的通用格式(掌握)
格式:
1
2
3
4
| public static 返回值类型 方法名(参数) {
方法体;
return 数据 ;
}
|
解释:
public static:修饰符,目前先记住这个格式
返回值类型:方法操作完毕之后返回的数据的数据类型
如果方法操作完毕,没有数据返回,这里写void,而且方法体中一般不写return
方法名:调用方法时候使用的标识
参数:由数据类型和变量名组成,多个参数之间用逗号隔开
方法体:完成功能的代码块
return:如果方法操作完毕,有数据返回,用于把数据返回给调用者
定义方法时,要做到两个明确
- 明确返回值类型:主要是明确方法操作完毕之后是否有数据返回,如果没有,写void;如果有,写对应的数据类型
- 明确参数:主要是明确参数的类型和数量
调用方法时的注意:
- void类型的方法,直接调用即可
- 非void类型的方法,推荐用变量接收调用
6. 方法重载
6.1 方法重载(理解)
方法重载指同一个类中定义的多个方法之间的关系,满足下列条件的多个方法相互构成重载
- 多个方法在同一个类中
- 多个方法具有相同的方法名
- 多个方法的参数不相同,类型不同或者数量不同
注意:
- 重载仅对应方法的定义,与方法的调用无关,调用方式参照标准格式
- 重载仅针对同一个类中方法的名称与参数进行识别,与返回值无关,换句话说不能通过返回值来判定两个方法是否相互构成重载
正确范例:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
| public class MethodDemo {
public static void fn(int a) {
}
public static int fn(double a) {
}
}
public class MethodDemo {
public static float fn(int a) {
}
public static int fn(int a , int b) {
}
}
|
错误范例:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
| public class MethodDemo {
public static void fn(int a) {
}
public static int fn(int a) {
}
}
public class MethodDemo01 {
public static void fn(int a) {
}
}
public class MethodDemo02 {
public static int fn(double a) {
}
}
|
6.2 方法重载练习(掌握)
需求:使用方法重载的思想,设计比较两个整数是否相同的方法,兼容全整数类型(byte,short,int,long)
思路:
- ①定义比较两个数字的是否相同的方法compare()方法,参数选择两个int型参数
- ②定义对应的重载方法,变更对应的参数类型,参数变更为两个long型参数
- ③定义所有的重载方法,两个byte类型与两个short类型参数
- ④完成方法的调用,测试运行结果
代码:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
| public class MethodTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println(compare(10, 20));
System.out.println(compare((byte) 10, (byte) 20));
System.out.println(compare((short) 10, (short) 20));
System.out.println(compare(10L, 20L));
}
public static boolean compare(int a, int b) {
System.out.println("int");
return a == b;
}
public static boolean compare(byte a, byte b) {
System.out.println("byte");
return a == b;
}
public static boolean compare(short a, short b) {
System.out.println("short");
return a == b;
}
public static boolean compare(long a, long b) {
System.out.println("long");
return a == b;
}
}
|
7. 方法的参数传递
7.1 方法参数传递基本类型(理解)
测试代码:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
| public class ArgsDemo01 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int number = 100;
System.out.println("调用change方法前:" + number);
change(number);
System.out.println("调用change方法后:" + number);
}
public static void change(int number) {
number = 200;
}
}
|
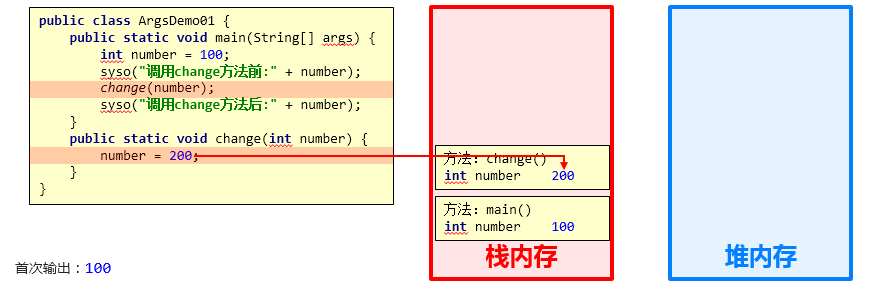
结论:基本数据类型的参数,形式参数的改变,不影响实际参数
结论依据:每个方法在栈内存中,都会有独立的栈空间,方法运行结束后就会弹栈消失
7.2 方法参数传递引用类型(理解)
测试代码:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
| public class ArgsDemo02 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] arr = {10, 20, 30};
System.out.println("调用change方法前:" + arr[1]);
change(arr);
System.out.println("调用change方法后:" + arr[1]);
}
public static void change(int[] arr) {
arr[1] = 200;
}
}
|
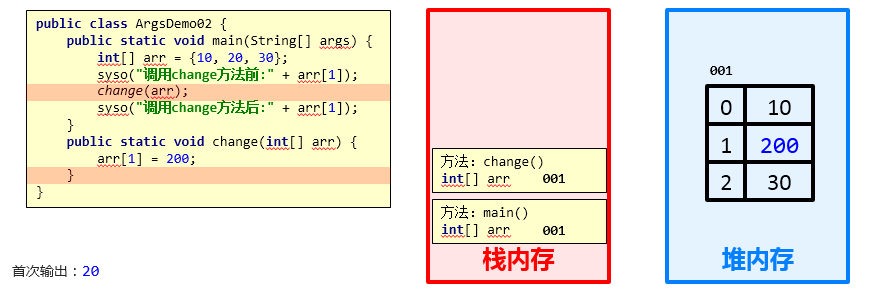
结论:对于引用类型的参数,形式参数的改变,影响实际参数的值
结论依据:引用数据类型的传参,传入的是地址值,内存中会造成两个引用指向同一个内存的效果,所以即使方法弹栈,堆内存中的数据也已经是改变后的结果。
7.3 数组遍历(应用)
需求:设计一个方法用于数组遍历,要求遍历的结果是在一行上的。例如:[11, 22, 33, 44, 55]
思路:
代码:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
| public class MethodTest01 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] arr = {11, 22, 33, 44, 55};
printArray(arr);
}
public static void printArray(int[] arr) {
System.out.print("[");
for(int x=0; x<arr.length; x++) {
if(x == arr.length-1) {
System.out.print(arr[x]);
} else {
System.out.print(arr[x]+", ");
}
}
System.out.println("]");
}
}
|
7.4 数组最大值(应用)
需求:设计一个方法用于获取数组中元素的最大值
思路:
- ①定义一个数组,用静态初始化完成数组元素初始化
- ②定义一个方法,用来获取数组中的最大值,最值的认知和讲解我们在数组中已经讲解过了
- ③调用获取最大值方法,用变量接收返回结果
- ④把结果输出在控制台
代码:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
| public class MethodTest02 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] arr = {12, 45, 98, 73, 60};
int number = getMax(arr);
System.out.println("number:" + number);
}
public static int getMax(int[] arr) {
int max = arr[0];
for(int x=1; x<arr.length; x++) {
if(arr[x] > max) {
max = arr[x];
}
}
return max;
}
}
|


