013-包装类&异常
1.包装类
1.1基本类型包装类(记忆)
基本类型包装类的作用
将基本数据类型封装成对象的好处在于可以在对象中定义更多的功能方法操作该数据
常用的操作之一:用于基本数据类型与字符串之间的转换
基本类型对应的包装类
| 基本数据类型 | 包装类 |
|---|---|
| byte | Byte |
| short | Short |
| int | Integer |
| long | Long |
| float | Float |
| double | Double |
| char | Character |
| boolean | Boolean |
1.2Integer类(应用)
Integer类概述
包装一个对象中的原始类型 int 的值
Integer类构造方法
| 方法名 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| public Integer(int value) | 根据 int 值创建 Integer 对象(过时) |
| public Integer(String s) | 根据 String 值创建 Integer 对象(过时) |
| public static Integer valueOf(int i) | 返回表示指定的 int 值的 Integer 实例 |
| public static Integer valueOf(String s) | 返回一个保存指定值的 Integer 对象 String |
示例代码
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21public class IntegerDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//public Integer(int value):根据 int 值创建 Integer 对象(过时)
Integer i1 = new Integer(100);
System.out.println(i1);
//public Integer(String s):根据 String 值创建 Integer 对象(过时)
Integer i2 = new Integer("100");
// Integer i2 = new Integer("abc"); //NumberFormatException
System.out.println(i2);
System.out.println("--------");
//public static Integer valueOf(int i):返回表示指定的 int 值的 Integer 实例
Integer i3 = Integer.valueOf(100);
System.out.println(i3);
//public static Integer valueOf(String s):返回一个保存指定值的Integer对象 String
Integer i4 = Integer.valueOf("100");
System.out.println(i4);
}
}
1.3int和String类型的相互转换(记忆)
int转换为String
转换方式
- 方式一:直接在数字后加一个空字符串
- 方式二:通过String类静态方法valueOf()
示例代码
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14public class IntegerDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//int --- String
int number = 100;
//方式1
String s1 = number + "";
System.out.println(s1);
//方式2
//public static String valueOf(int i)
String s2 = String.valueOf(number);
System.out.println(s2);
System.out.println("--------");
}
}
String转换为int
转换方式
- 方式一:先将字符串数字转成Integer,再调用 intValue()方法
- 方式二:通过Integer静态方法parseInt()进行转换
示例代码
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15public class IntegerDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//String --- int
String s = "100";
//方式1:String --- Integer --- int
Integer i = Integer.valueOf(s);
//public int intValue()
int x = i.intValue();
System.out.println(x);
//方式2
//public static int parseInt(String s)
int y = Integer.parseInt(s);
System.out.println(y);
}
}
1.4字符串数据排序案例(应用)
案例需求
有一个字符串:“91 27 46 38 50”,请写程序实现最终输出结果是:“27 38 46 50 91”
代码实现
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35public class IntegerTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//定义一个字符串
String s = "91 27 46 38 50";
//把字符串中的数字数据存储到一个int类型的数组中
String[] strArray = s.split(" ");
// for(int i=0; i<strArray.length; i++) {
// System.out.println(strArray[i]);
// }
//定义一个int数组,把 String[] 数组中的每一个元素存储到 int 数组中
int[] arr = new int[strArray.length];
for(int i=0; i<arr.length; i++) {
arr[i] = Integer.parseInt(strArray[i]);
}
//对 int 数组进行排序
Arrays.sort(arr);
//把排序后的int数组中的元素进行拼接得到一个字符串,这里拼接采用StringBuilder来实现
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
for(int i=0; i<arr.length; i++) {
if(i == arr.length - 1) {
sb.append(arr[i]);
} else {
sb.append(arr[i]).append(" ");
}
}
String result = sb.toString();
//输出结果
System.out.println(result);
}
}
1.5自动拆箱和自动装箱(理解)
自动装箱
把基本数据类型转换为对应的包装类类型
自动拆箱
把包装类类型转换为对应的基本数据类型
示例代码
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22public class IntegerDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 装箱:把基本数据类型转换为对应的包装类类型
Integer i = Integer.valueOf(100);
Integer ii = 100; //自动装箱,默认会调用Integer.valueOf(100);
// ii += 200;
// ii = ii + 200;
// ii = ii.intValue() + 200;
// ii = 300;
ii += 200;
System.out.println(ii);
Integer iii = null;
// iii += 100; //NullPointerException
if(iii != null) {
iii += 100;
}
}
}
// Integer i = 100; // 自动装箱
// i += 200; // i = i + 200; i + 200 自动拆箱;i = i + 200; 是自动装箱注意:只要是对象,在使用前,必须进行不为 null 的判断。
3.异常
3.1异常(记忆)
异常的概述
异常就是程序出现了不正常的情况
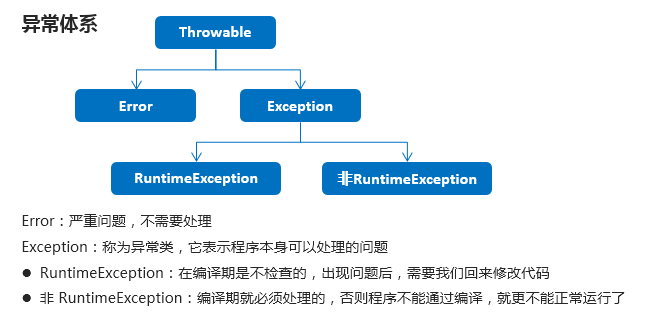
异常的体系结构
3.2JVM默认处理异常的方式(理解)
如果程序出现了问题,我们没有做任何处理,最终JVM 会做默认的处理,处理方式有如下两个步骤:
- 把异常的名称,错误原因及异常出现的位置等信息输出在了控制台
- 程序停止执行
3.3try-catch方式处理异常(应用)
定义格式
1
2
3
4
5try {
可能出现异常的代码;
} catch(异常类名 变量名) {
异常的处理代码;
}执行流程
- 程序从 try 里面的代码开始执行
- 出现异常,会自动生成一个异常类对象,该异常对象会被提交到Java运行时系统
- 当java运行时系统接受到异常对象时,会到catch中去找匹配的异常类,找到后运行相应的处理
- 执行完毕之后,程序还可以继续往下执行
示例代码
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18public class ExceptionDemo01 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("开始");
method();
System.out.println("结束");
}
public static void method() {
try {
int[] arr = {1, 2, 3};
System.out.println(arr[3]);
System.out.println("这里能够访问到吗");
} catch (ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException e) {
// System.out.println("你访问的数组索引不存在,请回去修改为正确的索引");
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
3.4Throwable成员方法(应用)
- 常用方法
| 方法名 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| public String getMessage() | 返回此 throwable 的详细消息字符串 |
| public String toString() | 返回此可抛出的简短描述 |
| public void printStackTrace() | 把异常的错误信息输出在控制台 |
示例代码
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30public class ExceptionDemo02 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("开始");
method();
System.out.println("结束");
}
public static void method() {
try {
int[] arr = {1, 2, 3};
System.out.println(arr[3]); //new ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException();
System.out.println("这里能够访问到吗");
} catch (ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException e) { //new ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException();
//public String getMessage():返回此 throwable 的详细消息字符串
// System.out.println(e.getMessage());
//Index 3 out of bounds for length 3
//public String toString():返回此可抛出的简短描述
// System.out.println(e.toString());
//java.lang.ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException: Index 3 out of bounds for length 3
//public void printStackTrace():把异常的错误信息输出在控制台
e.printStackTrace();
// java.lang.ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException: Index 3 out of bounds for length 3
// at com.itheima_02.ExceptionDemo02.method(ExceptionDemo02.java:18)
// at com.itheima_02.ExceptionDemo02.main(ExceptionDemo02.java:11)
}
}
}
3.5编译时异常和运行时异常的区别(记忆)
编译时异常(受检异常)
- 都是Exception类及其子类
- 必须显示处理,否则程序就会发生错误,无法通过编译
运行时异常(非受检异常)
- 都是RuntimeException类及其子类
- 无需显示处理,也可以和编译时异常一样处理
3.6throws方式处理异常(应用)
虽然我们可以通过 try..catch 进行异常处理,但并不是所有的情况我们都有权限进行异常处理,比如我只写方法,但是调用方法的代码不是我写
针对这种情况,我们可以使用throws 的方式进行处理
定义格式
1
2
3public void 方法() throws 异常类名 {
}示例代码
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26public class ExceptionDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("开始");
// method();
try {
method2();
}catch (ParseException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("结束");
}
//编译时异常
public static void method2() throws ParseException {
String s = "2048-08-09";
SimpleDateFormat sdf = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd");
Date d = sdf.parse(s);
System.out.println(d);
}
//运行时异常
public static void method() throws ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException {
int[] arr = {1, 2, 3};
System.out.println(arr[3]);
}
}注意事项
- 这个throws格式是跟在方法的括号后面的
- 编译时异常必须要进行处理,两种处理方案:try…catch …或者 throws,如果采用 throws 这种方案,将来谁调用谁处理
- 运行时异常可以不处理,出现问题后,需要我们回来修改代码
3.7throws和throw的区别(记忆)
- throws 是捕获异常
- throw 是主动抛出异常

3.8自定义异常(应用)
自定义异常类格式
1
2
3
4public class 异常类名 extends Exception {
无参构造函数
带参构造函数
}自定义异常类
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9public class ScoreException extends Exception {
public ScoreException() {}
public ScoreException(String message) {
super(message);
}
}老师类
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10public class Teacher {
public void checkScore(int score) throws ScoreException {
if(score<0 || score>100) {
// throw new ScoreException();
throw new ScoreException("你给的分数有误,分数应该在0-100之间");
} else {
System.out.println("成绩正常");
}
}
}测试类
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15public class Demo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("请输入分数:");
int score = sc.nextInt();
Teacher t = new Teacher();
try {
t.checkScore(score);
} catch (ScoreException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
013-包装类&异常
https://flepeng.github.io/021-Java-01-course-013-包装类-异常/