1 Spring Data JPA 的概述 1.1 Spring Data JPA 概述 Spring Data JPA 是 Spring 基于 ORM 框架、JPA 规范的基础上封装的一套 JPA 应用框架,可使开发者用极简的代码即可实现对数据库的访问和操作。它提供了包括增删改查等在内的常用功能,且易于扩展!学习并使用 Spring Data JPA 可以极大提高开发效率!
Spring Data JPA 让我们解脱了 DAO 层的操作,基本上所有 CRUD 都可以依赖于它来实现,在实际的工作工程中,推荐使用 Spring Data JPA + ORM(如:hibernate) 完成操作,这样在切换不同的 ORM 框架时提供了极大的方便,同时也使数据库层操作更加简单,方便解耦
1.2 Spring Data JPA 的特性 Spring Data Jpa 极大简化了数据库访问层代码。
如何简化的呢?使用了 Spring Data Jpa,我们的 dao 层中只需要写接口,就自动具有了增删改查、分页查询等方法。
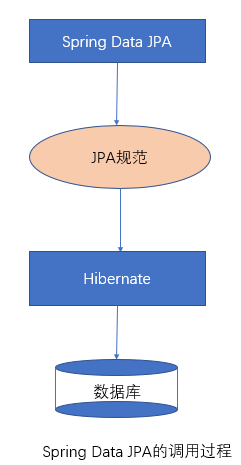
1.3 Spring Data JPA 与 JPA 和 Hibernate 之间的关系 JPA 是一套规范,内部是有接口和抽象类组成的。Hibernate 是一套成熟的 ORM 框架,而且 Hibernate 实现了 JPA 规范,所以也可以称 hibernate 为 JPA 的一种实现方式,我们使用 JPA 的 API 编程,意味着站在更高的角度上看待问题(面向接口编程)
Spring Data JPA 是 Spring 提供的一套对 JPA 操作更加高级的封装,是在 JPA 规范下的专门用来进行数据持久化的解决方案。
2 Spring Data JPA 的快速入门 2.1 需求说明 Spring Data JPA 完成客户的基本 CRUD 操作
2.2 搭建 Spring Data JPA 的开发环境 2.2.1 引入 Spring Data JPA 的坐标 使用 Spring Data JPA,需要整合 Spring 与 Spring Data JPA,并且需要提供 JPA 的服务提供者 hibernate,所以需要导入 spring 相关坐标,hibernate 坐标,数据库驱动坐标等
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 124 125 126 127 128 129 130 131 132 133 134 135 136 137 138 139 140 141 142 143 <project > <properties > <spring.version > 4.2.4.RELEASE</spring.version > <hibernate.version > 5.0.7.Final</hibernate.version > <slf4j.version > 1.6.6</slf4j.version > <log4j.version > 1.2.12</log4j.version > <c3p0.version > 0.9.1.2</c3p0.version > <mysql.version > 5.1.6</mysql.version > </properties > <dependencies > <dependency > <groupId > junit</groupId > <artifactId > junit</artifactId > <version > 4.9</version > <scope > test</scope > </dependency > <dependency > <groupId > org.aspectj</groupId > <artifactId > aspectjweaver</artifactId > <version > 1.6.8</version > </dependency > <dependency > <groupId > org.springframework</groupId > <artifactId > spring-aop</artifactId > <version > ${spring.version}</version > </dependency > <dependency > <groupId > org.springframework</groupId > <artifactId > spring-context</artifactId > <version > ${spring.version}</version > </dependency > <dependency > <groupId > org.springframework</groupId > <artifactId > spring-context-support</artifactId > <version > ${spring.version}</version > </dependency > <dependency > <groupId > org.springframework</groupId > <artifactId > spring-orm</artifactId > <version > ${spring.version}</version > </dependency > <dependency > <groupId > org.springframework</groupId > <artifactId > spring-beans</artifactId > <version > ${spring.version}</version > </dependency > <dependency > <groupId > org.springframework</groupId > <artifactId > spring-core</artifactId > <version > ${spring.version}</version > </dependency > <dependency > <groupId > org.hibernate</groupId > <artifactId > hibernate-core</artifactId > <version > ${hibernate.version}</version > </dependency > <dependency > <groupId > org.hibernate</groupId > <artifactId > hibernate-entitymanager</artifactId > <version > ${hibernate.version}</version > </dependency > <dependency > <groupId > org.hibernate</groupId > <artifactId > hibernate-validator</artifactId > <version > 5.2.1.Final</version > </dependency > <dependency > <groupId > c3p0</groupId > <artifactId > c3p0</artifactId > <version > ${c3p0.version}</version > </dependency > <dependency > <groupId > log4j</groupId > <artifactId > log4j</artifactId > <version > ${log4j.version}</version > </dependency > <dependency > <groupId > org.slf4j</groupId > <artifactId > slf4j-api</artifactId > <version > ${slf4j.version}</version > </dependency > <dependency > <groupId > org.slf4j</groupId > <artifactId > slf4j-log4j12</artifactId > <version > ${slf4j.version}</version > </dependency > <dependency > <groupId > mysql</groupId > <artifactId > mysql-connector-java</artifactId > <version > ${mysql.version}</version > </dependency > <dependency > <groupId > org.springframework.data</groupId > <artifactId > spring-data-jpa</artifactId > <version > 1.9.0.RELEASE</version > </dependency > <dependency > <groupId > org.springframework</groupId > <artifactId > spring-test</artifactId > <version > 4.2.4.RELEASE</version > </dependency > <dependency > <groupId > javax.el</groupId > <artifactId > javax.el-api</artifactId > <version > 2.2.4</version > </dependency > <dependency > <groupId > org.glassfish.web</groupId > <artifactId > javax.el</artifactId > <version > 2.2.4</version > </dependency > </dependencies > </project >
2.2.2 整合 Spring Data JPA 与 Spring 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 <?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <beans xmlns ="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi ="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns:aop ="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop" xmlns:context ="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context" xmlns:jdbc ="http://www.springframework.org/schema/jdbc" xmlns:tx ="http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx" xmlns:jpa ="http://www.springframework.org/schema/data/jpa" xmlns:task ="http://www.springframework.org/schema/task" xsi:schemaLocation =" http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/jdbc http://www.springframework.org/schema/jdbc/spring-jdbc.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx/spring-tx.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/data/jpa http://www.springframework.org/schema/data/jpa/spring-jpa.xsd" ><bean id ="dataSource" class ="com.mchange.v2.c3p0.ComboPooledDataSource" > <property name ="driverClass" value ="com.mysql.jdbc.Driver" /> <property name ="jdbcUrl" value ="jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/jpa" /> <property name ="user" value ="root" /> <property name ="password" value ="111111" /> </bean > <bean id ="entityManagerFactory" class ="org.springframework.orm.jpa.LocalContainerEntityManagerFactoryBean" > <property name ="dataSource" ref ="dataSource" /> <property name ="packagesToScan" value ="cn.itcast.entity" /> <property name ="persistenceProvider" > <bean class ="org.hibernate.jpa.HibernatePersistenceProvider" /> </property > <property name ="jpaVendorAdapter" > <bean class ="org.springframework.orm.jpa.vendor.HibernateJpaVendorAdapter" > <property name ="generateDdl" value ="false" /> <property name ="database" value ="MYSQL" /> <property name ="databasePlatform" value ="org.hibernate.dialect.MySQLDialect" /> <property name ="showSql" value ="true" /> </bean > </property > <property name ="jpaDialect" > <bean class ="org.springframework.orm.jpa.vendor.HibernateJpaDialect" /> </property > </bean > <bean id ="transactionManager" class ="org.springframework.orm.jpa.JpaTransactionManager" > <property name ="entityManagerFactory" ref ="entityManagerFactory" /> </bean > <jpa:repositories base-package ="cn.itcast.dao" transaction-manager-ref ="transactionManager" entity-manager-factory-ref ="entityManagerFactory" > </jpa:repositories > <tx:advice id ="txAdvice" transaction-manager ="transactionManager" > <tx:attributes > <tx:method name ="save*" propagation ="REQUIRED" /> <tx:method name ="insert*" propagation ="REQUIRED" /> <tx:method name ="update*" propagation ="REQUIRED" /> <tx:method name ="delete*" propagation ="REQUIRED" /> <tx:method name ="get*" read-only ="true" /> <tx:method name ="find*" read-only ="true" /> <tx:method name ="*" propagation ="REQUIRED" /> </tx:attributes > </tx:advice > <aop:config > <aop:pointcut id ="pointcut" expression ="execution(* cn.itcast.service.*.*(..))" /> <aop:advisor advice-ref ="txAdvice" pointcut-ref ="pointcut" /> </aop:config > <context:component-scan base-package ="cn.itcast" > </context:component-scan > </beans >
2.2.3 使用 JPA 注解配置映射关系 我们使用昨天案例中的Customer实体类对象,已经配置好了映射关系
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 package cn.itcast.entity;import javax.persistence.Column;import javax.persistence.Entity;import javax.persistence.GeneratedValue;import javax.persistence.GenerationType;import javax.persistence.Id;import javax.persistence.Table;@Entity @Table (name="cst_customer" ) public class Customer @Id @GeneratedValue (strategy=GenerationType.IDENTITY) @Column (name="cust_id" ) private Long custId;@Column (name="cust_name" ) private String custName;@Column (name="cust_source" ) private String custSource;@Column (name="cust_industry" )private String custIndustry;@Column (name="cust_level" ) private String custLevel;@Column (name="cust_address" )private String custAddress;@Column (name="cust_phone" ) private String custPhone;
2.3 使用 Spring Data JPA 完成需求 2.3.1 编写符合 Spring Data JPA 规范的Dao层接口 Spring Data JPA 是 spring 提供的一款对于数据访问层(Dao层)的框架,使用 Spring Data JPA,只需要按照框架的规范提供 dao 接口,不需要实现类就可以完成数据库的增删改查、分页查询等方法的定义,极大的简化了我们的开发过程。
在 Spring Data JPA 中,对于定义符合规范的 Dao 层接口,我们只需要遵循以下几点就可以了:
创建一个 Dao 层接口,并实现 JpaRepository 和 JpaSpecificationExecutor
提供相应的泛型
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 package cn.itcast.dao;import java.util.List;import org.springframework.data.jpa.repository.JpaRepository;import org.springframework.data.jpa.repository.JpaSpecificationExecutor;import cn.itcast.entity.Customer;public interface CustomerDao extends JpaRepository <Customer , Long >, JpaSpecificationExecutor <Customer >
这样我们就定义好了一个符合 Spring Data JPA 规范的Dao层接口
2.3.2 完成基本 CRUD 操作 完成了 Spring Data JPA 的环境搭建,并且编写了符合 Spring Data JPA 规范的 Dao 层接口之后,就可以使用定义好的 Dao 层接口进行客户的基本 CRUD 操作
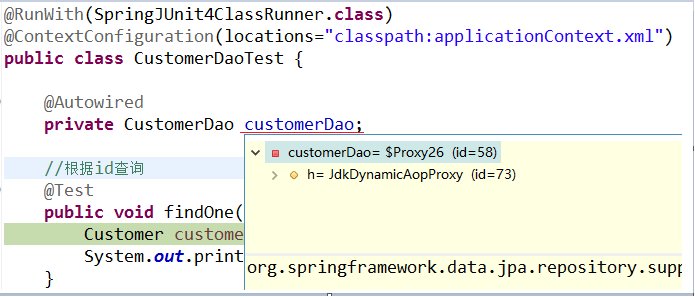
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 @RunWith (SpringJUnit4ClassRunner.class ) @ContextConfiguration (locations ="classpath:applicationContext.xml" )public class CustomerDaoTest @Autowired private CustomerDao customerDao;@Test public void testSave () new Customer();"传智播客" );@Test public void testFindById () 2l );@Test public void testUpdate () 1l );"传智播客顺义校区" );@Test public void testDelete () 1l );
3 Spring Data JPA 的内部原理剖析 3.1 Spring Data JPA 的常用接口分析 在客户的案例中,我们发现在自定义的 CustomerDao中,并没有提供任何方法就可以使用其中的很多方法,那么这些方法究竟是怎么来的呢?答案很简单,对于我们自定义的 Dao 接口,由于继承了 JpaRepository 和 JpaSpecificationExecutor,所以我们可以使用这两个接口的所有方法。
在使用 Spring Data JPA 时,一般实现 JpaRepository 和 JpaSpecificationExecutor 接口,这样就可以使用这些接口中定义的方法,但是这些方法都只是一些声明,没有具体的实现方式,那么在 Spring Data JPA 中它又是怎么实现的呢?
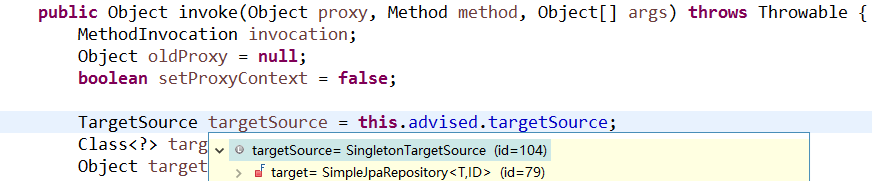
3.2 Spring Data JPA 的实现过程 通过对客户案例,以 debug 断点调试的方式,通过分析 Spring Data JPA 的源码来分析程序的执行过程。我们以 findOne 方法为例进行分析:
代理子类的实现过程
代理对象中方法调用的分析
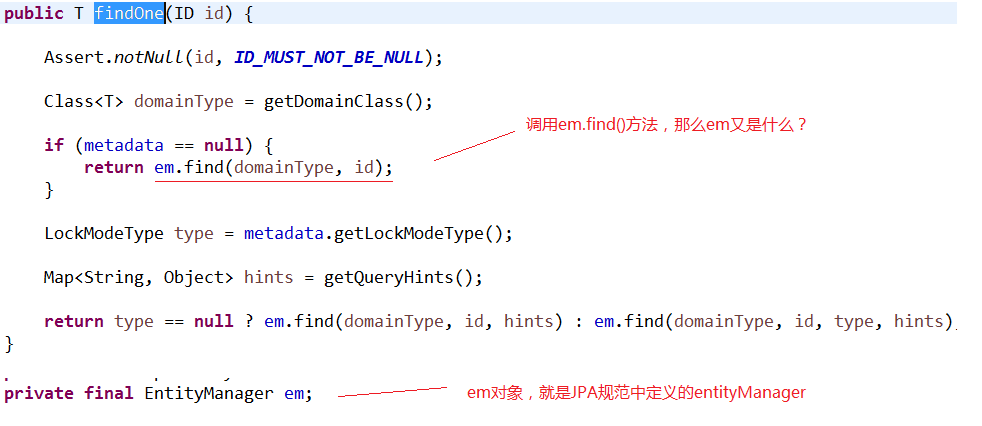
通过 SimpleJpaRepository 的源码分析,定位到了 findOne 方法,在此方法中,返回 em.find() 的返回结果,那么em又是什么呢?
3.3 Spring Data JPA 完整的调用过程分析
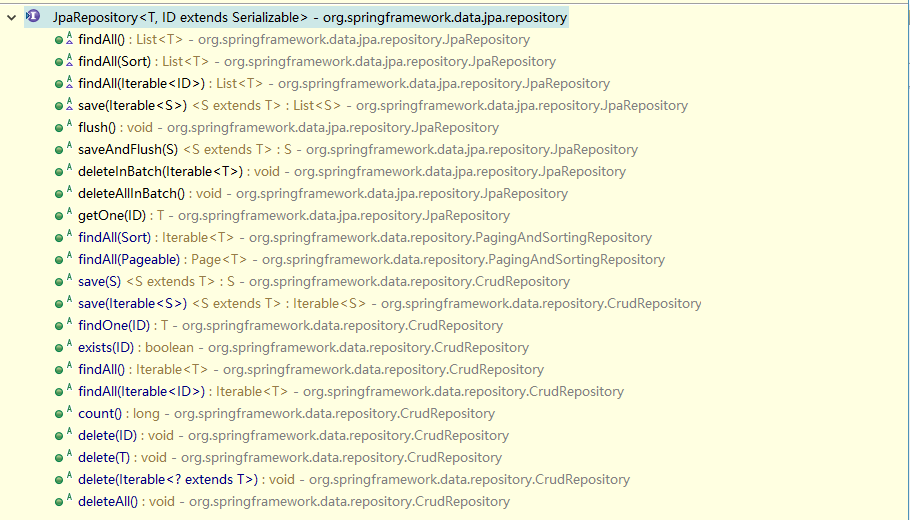
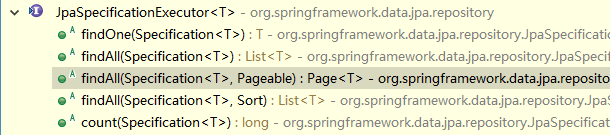
4 Spring Data JPA 的查询方式 4.1 使用 Spring Data JPA 中接口定义的方法进行查询 在继承 JpaRepository 和 JpaSpecificationExecutor 接口后,我们就可以使用接口中定义的方法进行查询
继承 JpaRepository 后的方法列表
继承 JpaSpecificationExecutor 的方法列表
4.2 使用 JPQL 的方式查询 使用 Spring Data JPA 提供的查询方法已经可以解决大部分的应用场景,但是对于某些业务来说,我们还需要灵活的构造查询条件,这时就可以使用 @Query 注解,结合 JPQL 的语句方式完成查询
@Query 注解的使用非常简单,只需在方法上面标注该注解,同时提供一个 JPQL 查询语句即可
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 public interface CustomerDao extends JpaRepository <Customer , Long >,JpaSpecificationExecutor <Customer > @Query (value="from Customer" )public List<Customer> findAllCustomer () @Query (value="from Customer where custName = ?1" )public Customer findCustomer (String custName)
此外,也可以通过使用 @Query 来执行一个更新操作,为此,我们需要在使用 @Query 的同时,用 @Modifying 来将该操作标识为修改查询,这样框架最终会生成一个更新的操作,而非查询
1 2 3 @Query (value="update Customer set custName = ?1 where custId = ?2" )@Modifying
4.3 使用 SQL 语句查询 Spring Data JPA 同样也支持 SQL 语句的查询,如下:
1 2 3 4 5 value ="select * from cst_customer" ,nativeQuery=true ) public void findSql (
使用了 @Query,Jpa 会自动把查询结果封装到返回结果对象中
如果返回的是整张表数据,可以直接映射到实体类,用 Bean 或者 List<Bean> 皆可
返回的是统计数据,那么可以用Integer接收,或者其他的类,这是单个数据的返回值,也可以直接映射
当返回值是两列或多列数据时,可以用 Map 映射,如果是多行可以用 List<Map> 映射,这时候每一行都被映射成一个Map。
1 2 @Query (value = "SELECT x.*, y.name FROM table_1 x LEFT JOIN table_2 y ON x.table_2_id = y.id) List<Map> joinTables(String Id, String name);
dao 层中查询的结果只能是一种实体类型,如果 SQL 查询的是一个多表组合,如 join,结果则需要创建一个实体类,单独为这个定制实体类写一个dao层来持久化处理,如果不想写,也可以用上面的 List<Object> 来接受
@Query 和 page 结合,同时使用 Pageable 参数
1 2 @Query(value = "SELECT x.*, y.name FROM table_1 x LEFT JOIN table_2 y ON x.table_2_id = y.id)Map > joinTables(String Id , String name , Pageable pageable);
当需要使用 Pageable 利用字段排序时,如果在Java的代码中使用的实体类是用驼峰命名(createdTime),而在 MySQL 中用的是下划线命名(created_time),即在实体类中用了 @Column 进行映射。此时 Pageable 中的参数必须传入 MySQL 中的下划线命名,而不是实体类的驼峰命名。
4.4 方法命名规则查询 顾名思义,方法命名规则查询就是 根据方法的名字,就能创建查询 。只需要按照 Spring Data JPA 提供的方法命名规则定义方法的名称,就可以完成查询工作。Spring Data JPA 在程序执行的时候会根据方法名称进行解析,并自动生成查询语句进行查询
按照 Spring Data JPA 定义的规则,查询方法以 findBy 开头,涉及条件查询时,条件的属性用条件关键字连接,要注意的是:条件属性首字母需大写。框架在进行方法名解析时,会先把方法名多余的前缀截取掉,然后对剩下部分进行解析。
1 2 public Customer findByCustName (String custName)
具体的关键字,使用方法和生产成SQL如下表所示
Keyword
Sample
JPQL
And
findByLastnameAndFirstname
… where x.lastname = ?1 and x.firstname = ?2
Or
findByLastnameOrFirstname
… where x.lastname = ?1 or x.firstname = ?2
Is,Equals
findByFirstnameIs
findByFirstnameEquals
… where x.firstname = ?1
Between
findByStartDateBetween
… where x.startDate between ?1 and ?2
LessThan
findByAgeLessThan
… where x.age < ?1
LessThanEqual
findByAgeLessThanEqual
… where x.age ⇐ ?1
GreaterThan
findByAgeGreaterThan
… where x.age > ?1
GreaterThanEqual
findByAgeGreaterThanEqual
… where x.age >= ?1
After
findByStartDateAfter
… where x.startDate > ?1
Before
findByStartDateBefore
… where x.startDate < ?1
IsNull
findByAgeIsNull
… where x.age is null
IsNotNull,NotNull
findByAge(Is)NotNull
… where x.age not null
Like
findByFirstnameLike
… where x.firstname like ?1
NotLike
findByFirstnameNotLike
… where x.firstname not like ?1
StartingWith
findByFirstnameStartingWith
… where x.firstname like ?1 (parameter bound with appended %)
EndingWith
findByFirstnameEndingWith
… where x.firstname like ?1 (parameter bound with prepended %)
Containing
findByFirstnameContaining
… where x.firstname like ?1 (parameter bound wrapped in %)
OrderBy
findByAgeOrderByLastnameDesc
… where x.age = ?1 order by x.lastname desc
Not
findByLastnameNot
… where x.lastname <> ?1
In
findByAgeIn(Collection ages)
… where x.age in ?1
NotIn
findByAgeNotIn(Collection age)
… where x.age not in ?1
TRUE
findByActiveTrue()
… where x.active = true
FALSE
findByActiveFalse()
… where x.active = false
IgnoreCase
findByFirstnameIgnoreCase
… where UPPER(x.firstame) = UPPER(?1)