104-SpringBoot基础3-配置原理
4. 自动配置原理
使用Spring Boot之后,一个整合了SpringMVC的WEB工程开发,变的无比简单,那些繁杂的配置都消失不见了,这是如何做到的?
一切魔力的开始,都是从我们的main函数来的,所以我们再次来看下启动类:
1 | |
我们发现特别的地方有两个:
- 注解:
@SpringBootApplication:标注SpringBoot的启动类,该注解具备多种功能 - run方法:
SpringApplication.run():代表运行SpringBoot的启动类,参数为SpringBoot启动类的字节码对象
我们分别来研究这两个部分。
4.1. 了解 @SpringBootApplication
点击进入,查看源码:
1 | |
这里重点的注解有3个:
@SpringBootConfiguration@EnableAutoConfiguration@ComponentScan
4.1.1. @SpringBootConfiguration
1 | |
源码如上,在@SpringBootConfiguration 注解上面,又有一个 @Configuration 注解。
@Configuration 这个注解的作用就是声明当前类是一个配置类,然后Spring会自动扫描到添加了@Configuration的类,并且读取其中的配置信息。
而@SpringBootConfiguration是来声明当前类是SpringBoot应用的配置类,项目中只能有一个。所以一般我们无需自己添加。
4.1.2. @EnableAutoConfiguration
关于这个注解,官网上有一段说明,原文:
The second class-level annotation is @EnableAutoConfiguration .
This annotation tells Spring Boot to “guess” how you want to configure Spring, based on the jar dependencies that you have added.
Since spring-boot-starter-web added Tomcat and Spring MVC, the auto-configuration assumes that you are developing a web application and sets up Spring accordingly
简单翻译:第二级的注解@EnableAutoConfiguration,告诉Spring Boot基于你所添加的依赖,去“猜测”你想要如何配置Spring。
比如我们引入了spring-boot-starter-web,而这个启动器中帮我们添加了tomcat、SpringMVC 的依赖。此时自动配置就知道你是要开发一个web应用,所以就帮你完成了web及SpringMVC的默认配置了!
总结,Spring Boot内部对大量的第三方库或Spring内部库进行了默认配置,这些配置是否生效,取决于我们是否引入了对应库所需的依赖,如果引入了所需的依赖,那么默认配置就会生效。
所以,我们使用SpringBoot构建一个项目,只需要引入所需框架的依赖,配置就可以交给SpringBoot处理了。除非你不希望使用SpringBoot的默认配置,它也提供了自定义配置的入口。
按住Ctrl点击查看注解 @EnableAutoConfiguration
1 | |
其中,@Import(AutoConfigurationImportSelector.class) 导入了 AutoConfigurationImportSelector 类
按住Ctrl点击查看 AutoConfigurationImportSelector 源码
1 | |
其中,SpringFactoriesLoader.loadFactoryNames 方法的作用就是从 META-INF/spring.factories 文件中读取指定类对应的类名称列表
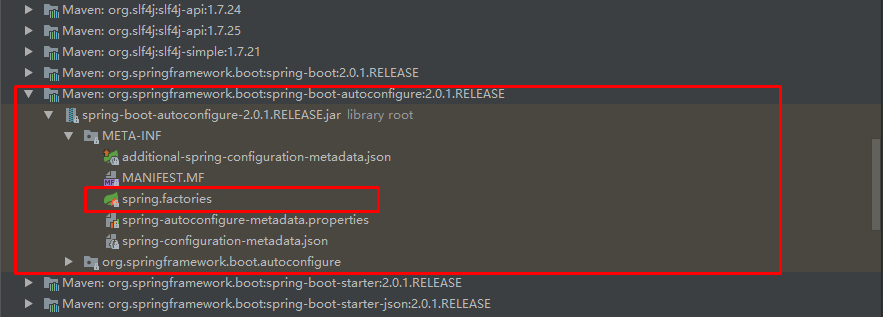
spring.factories 文件中有关自动配置的配置信息如下:
1 | |
上面配置文件存在大量的以Configuration为结尾的类名称,这些类就是存有自动配置信息的类,而SpringApplication在获取这些类名后再加载
我们以 ServletWebServerFactoryAutoConfiguration 为例来分析源码:
1 | |
其中,
@EnableConfigurationProperties(ServerProperties.class) 代表加载ServerProperties服务器配置属性类
进入ServerProperties.class源码如下:
1 | |
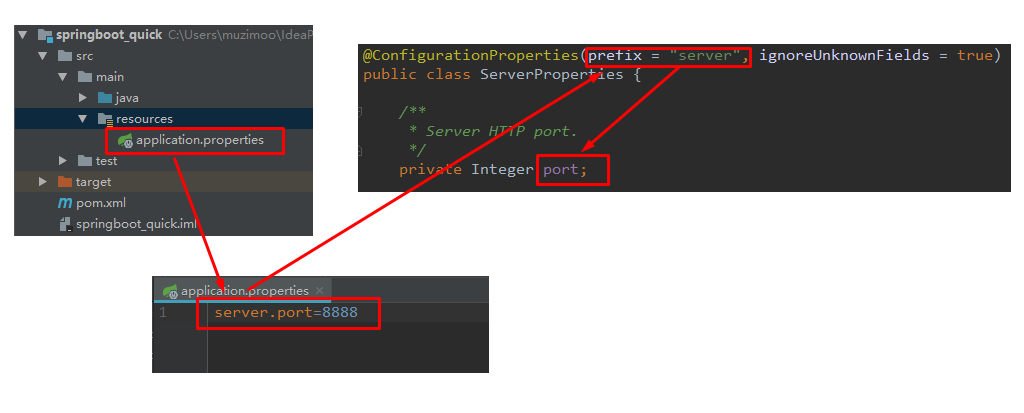
其中,
prefix = "server" 表示SpringBoot配置文件中的前缀,SpringBoot会将配置文件中以server开始的属性映射到该类的字段中。映射关系如下:
4.1.3. @ComponentScan
1 | |
源码如上。然后查看注释的意思为:配置组件扫描的指令。提供了类似与 <context:component-scan> 标签的作用。
通过
basePackageClasses或者basePackages属性来指定要扫描的包。如果没有指定这些属性,那么将从声明这个注解的类所在的包开始,扫描包及子包
而我们的 @SpringBootApplication 注解声明的类就是main函数所在的启动类,因此扫描的包是该类所在包及其子包。因此,一般启动类会放在一个比较靠前的包目录中。
4.2. 默认配置原理
4.2.1. spring.factories
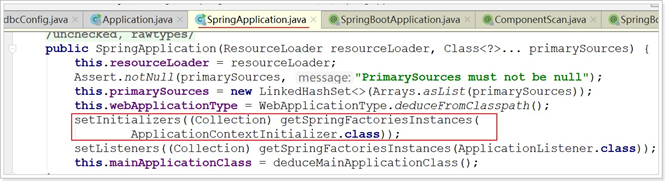
在SpringApplication类构建的时候,有这样一段初始化代码:
跟进去:
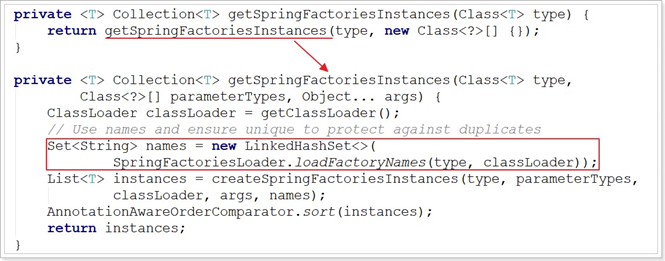
这里发现会通过loadFactoryNames尝试加载一些FactoryName,然后利用createSpringFactoriesInstances将这些加载到的类名进行实例化。
继续跟进loadFactoryNames方法:
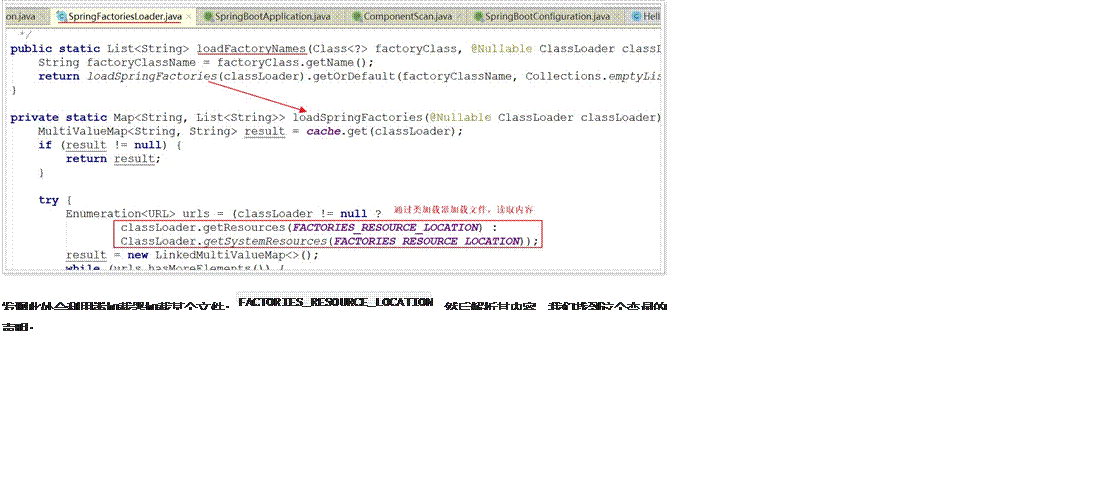
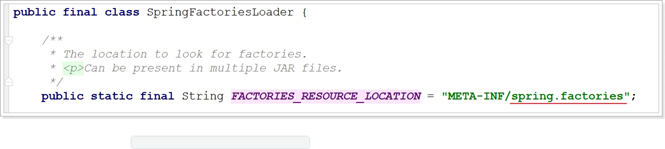
可以发现,其地址是: META-INF/spring.factories,我们知道,ClassLoader默认是从classpath下读取文件,因此,SpringBoot会在初始化的时候,加载所有classpath:META-INF/spring.factories文件,包括jar包当中的。而在Spring的一个依赖包:spring-boot-autoconfigure中,就有这样的文件:
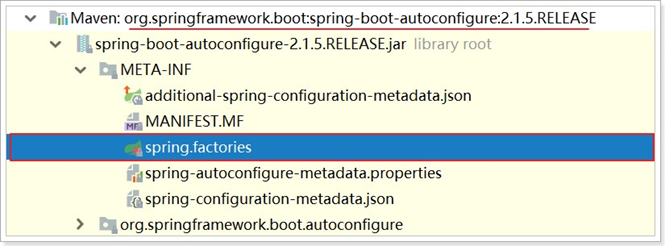
以后我们引入的任何第三方启动器,只要实现自动配置,也都会有类似文件。
4.2.1. 默认配置类
我们打开刚才的spring.factories文件:
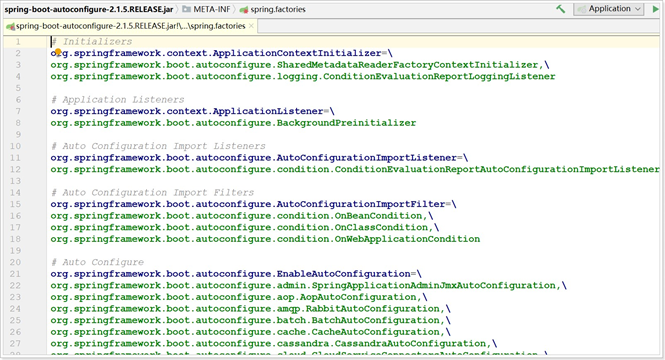
可以发现以EnableAutoConfiguration接口为key的一系列配置,key所对应的值,就是所有的自动配置类,可以在当前的jar包中找到这些自动配置类:

非常多,几乎涵盖了现在主流的开源框架,例如:
- redis
- jms amqp jdbc jackson
- mongodb jpa solr elasticsearch … 等等
我们来看一个我们熟悉的,例如SpringMVC,查看mvc 的自动配置类:
打开WebMvcAutoConfiguration:
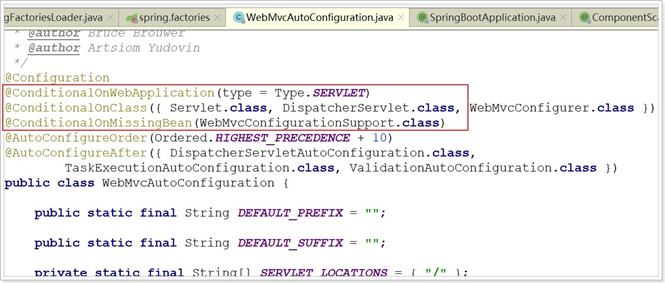
我们看到这个类上的4个注解:
@Configuration:声明这个类是一个配置类@ConditionalOnWebApplication(type = Type.SERVLET)
ConditionalOn,翻译就是在某个条件下,此处就是满足项目的类是是Type.SERVLET类型,也就是一个普通 web工程,显然我们就是@ConditionalOnClass({ Servlet.class, DispatcherServlet.class, WebMvcConfigurer.class })这里的条件是OnClass,也就是满足以下类存在:Servlet、DispatcherServlet、WebMvcConfigurer,其中 Servlet只要引入了tomcat依赖自然会有,后两个需要引入SpringMVC才会有。这里就是判断你是否引入了相关依赖,引入依赖后该条件成立,当前类的配置才会生效!@ConditionalOnMissingBean(WebMvcConfigurationSupport.class)
这个条件与上面不同,OnMissingBean,是说环境中没有指定的Bean这个才生效。其实这就是自定义配置的入口,也就是说,如果我们自己配置了一个WebMVCConfigurationSupport的类,那么这个默认配置就会失效!
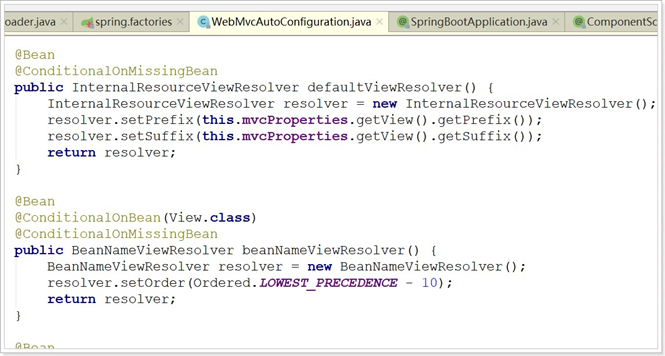
接着,我们查看该类中定义了什么:视图解析器:
处理器适配器(HandlerAdapter):
还有很多,这里就不一一截图了。
4.2.2. 默认配置属性
另外,这些默认配置的属性来自哪里呢?
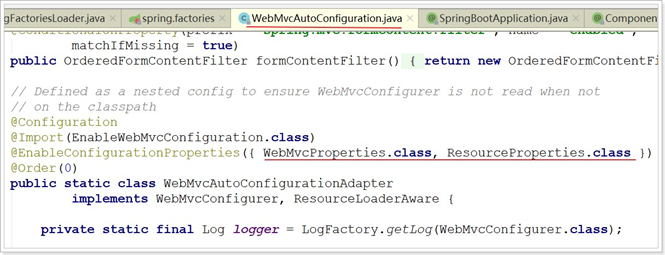
我们看到,这里通过@EnableAutoConfiguration注解引入了两个属性:WebMvcProperties和 ResourceProperties。这不正是SpringBoot的属性注入玩法嘛。
我们查看这两个属性类:
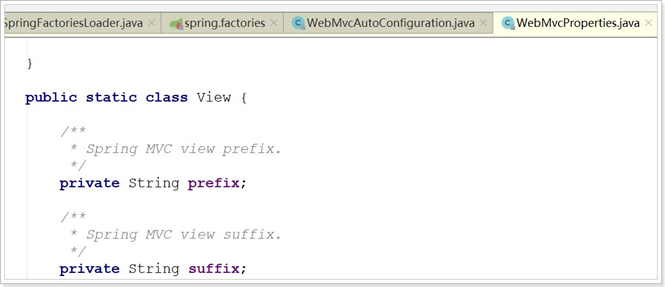
找到了内部资源视图解析器的prefix和suffix属性。
ResourceProperties中主要定义了静态资源(.js,.html,.css等)的路径:
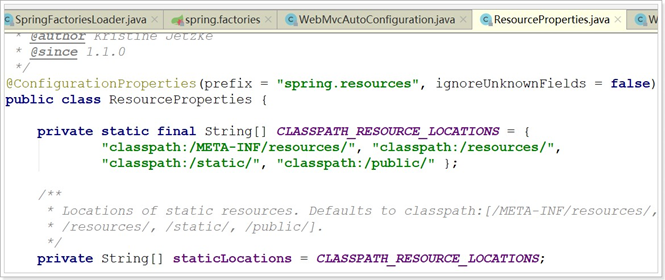
如果我们要覆盖这些默认属性,只需要在application.properties中定义与其前缀prefix和字段名一致的属性即可。
4.3. 总结
SpringBoot为我们提供了默认配置,而默认配置生效的步骤:
@EnableAutoConfiguration注解会去寻找META-INF/spring.factories文件,读取其中以EnableAutoConfiguration为key的所有类的名称,这些类就是提前写好的自动配置类这些类都声明了
@Configuration注解,并且通过@Bean注解提前配置了我们所需要的一切实例但是,这些配置不一定生效,因为有
@ConditionalOn注解,满足一定条件才会生效。比如条件之一:是一些相关的类要存在类要存在,我们只需要引入了相关依赖(启动器),依赖有了条件成立,自动配置生效。如果我们自己配置了相关Bean,那么会覆盖默认的自动配置的 Bean
我们还可以通过配置
application.yml文件,来覆盖自动配置中的属性
1)启动器
所以,我们如果不想配置,只需要引入依赖即可,而依赖版本我们也不用操心,因为只要引入了SpringBoot提供的 stater(启动器),就会自动管理依赖及版本了。
因此,玩SpringBoot的第一件事情,就是找启动器,SpringBoot提供了大量的默认启动器
2)全局配置
另外,SpringBoot的默认配置,都会读取默认属性,而这些属性可以通过自定义 application.properties 文件来进行覆盖。这样虽然使用的还是默认配置,但是配置中的值改成了我们自定义的。
因此,玩 SpringBoot 的第二件事情,就是通过 application.properties 来覆盖默认属性值,形成自定义配置。我们需要知道 SpringBoot 的默认属性 key,非常多,可以再idea中自动提示
属性文件支持两种格式,application.properties 和 application.yml yml的语法实例:
- 如果properties和yml文件都存在,如果有重叠属性,默认以Properties优先。遇到需要修改的组件的配置项流程为: